


Unlike most other methods, PGTseq-A combines two distinct pieces of information to provide unparalleled accuracy. The test simultaneously assesses the quantity of DNA at numerous sites on each chromosome using an advanced next generation sequencing method and combines this information with analysis of DNA sequence variations, which provide an independent evaluation of chromosome copy number.
25,007 embryos analyzed.
%transferable per informative embryo
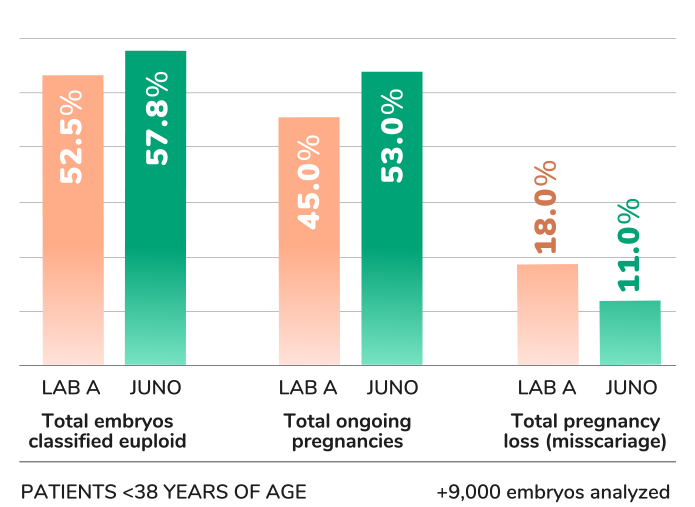
Juno uses a unique PGTseq-A methodology, which is the only method in the world to have successfully demonstrated clinical validity in a non-selectin study.
Our PGTseq-A strategy employs the latest next-generation sequencing methods, increasing the quality of the data obtained and yielding results of unparalleled accuracy.






At Juno we offer you the possibility of connecting our management and reporting system with the system at your clinic. This will mean you are permanently connected and will have real-time information on the current process and status of your sample.
Juno Genetics harnesses the power of the very latest DNA sequencing technologies to deliver a best-in-class test for chromosome abnormalities, called PGTseq-A. Not only does PGTseq-A measure the amount of DNA from each chromosome with unprecedented accuracy, allowing the number of copies of each chromosome to be determined in the embryo biopsy specimen, but it also detects thousands of variations in the sequence of the DNA from the embryo (known as polymorphisms). Juno was one of the first laboratories in the world to add polymorphism analysis to a PGT-A test. The extra information provided by DNA polymorphisms allows detection of important chromosome abnormalities that are invisible to other PGT-A methods, including triploidy, a common cause of miscarriage. Clinical studies have shown that the Juno PGTseq-A method succeeds in providing valuable predictive information about an embryo’s capacity to produce a healthy birth, helping to avoid the transfer of abnormal embryos, which will fail to implant, miscarry or produce children affected by chromosomal abnormalities.